| Channel | Publish Date | Thumbnail & View Count | Download Video |
|---|---|---|---|
| | Publish Date not found | 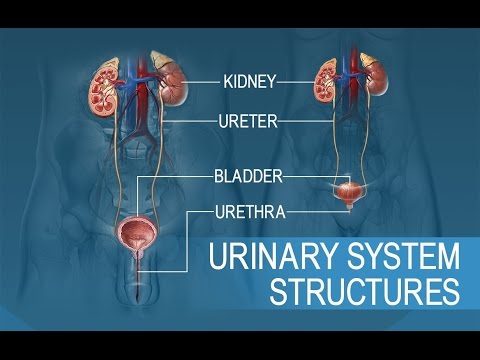 0 Views |
urinary tract infection kidney infection bladder infection bladder cancer bladder infection symptoms urinary tract infection human body parts urinary tract infections bladder cancer symptoms urinary incontinence urinary tract infection symptoms human digestive system antibiotics for urinary tract infections bladder infection symptoms urinary tract infection urinary tract infection treatment urinary tract infection symptoms bladder problems urinary bladder infection treatment urinary tract infection causes anatomy of the human body human body anatomy bladder infection in men urinary tract infection bladder infection treatment uti bladder infection causes urinary tract infection in women urinary tract infection symptoms urinary tract infection in men urinary system diseases bladder problems in women urinary tract infection symptoms anatomy and physiology of women treatment of bladder infection urinary infections anatomy and physiology of Saladin function of the urinary system anatomy and physiology function of the urinary system of Saladin function of the urinary system what is the function of the urinary system treatment of urinary system infections human urinary tract female urinary tract bladder infections in women urinary tract infection in men bladder infection
#Anatomy#Physiology#Urinary
00:00 Presentation
0:05 Functions of the urinary system Removes metabolic waste Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Regulates plasma concentrations of sodium, potassium chloride, etc. Helps stabilize blood pH Retains valuable nutrients
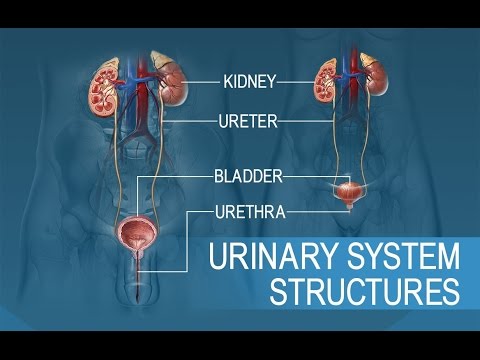
1:52 Urinary System Organs/Tissues Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra
2:47 Renal anatomy 2 kidneys, on each side of the spine between T2 and L, the left kidney is slightly higher than the right • Stabilized in place by surrounding connective tissue Reddish brown, approximately 10 cm long, 5.5 cm wide and 3 cm thick, with a mass of 150 g • Renal cortex Renal marrow Renal pyramid Major/minor calyx
6:41 Blood flow to the kidneys • In healthy individuals, more than a liter of blood flows through the kidneys every minute! Receive blood through the renal arteries – Segmental arteries, interlobar arteries, arcuate arteries… afferent arterioles supply the nephrons • Blood exits through the renal veins
9:27 Nephrons Microscopic tubular structures in the cortex of the kidneys that filter blood and produce urine • 1.25 million nephrons per kidney!
12:40 Glomerular filtration Glomerular capillaries are fenestrated Blood pressure forces water and small solutes through the membrane and into the capsular space • Some important nutrients (glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, vitamins) can also pass through – These are reabsorbed into the PCT
17:28 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Differs from PCT due to its small diameter and absence of microvilli Important for 3 basic processes: – Actively secretes ions, acids, drugs, toxins – Selectively absorbs sodium and calcium ions – Selectively absorbs water
6:35 p.m. Collecting system Some final filtrations, secretions and reabsorptions. Now the concentrated urine passes through the collecting duct, which merges into the papillary ducts. • The liquid empties into the minor chalice which leads
Around 9:16 p.m. 95% water…what else is in it? Urea: very abundant, resulting from the degradation of amino acids – Creatinine: resulting from the degradation of creatine phosphate (from muscles) – Uric acid: formed from the recycling of nitrogenous bases of RNA – Urobilin: a by-product of
24:55 Ureters • Pair of muscular tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder Firmly attached to the posterior abdominal wall – 3 layers of tissue: inner mucosa, muscular layer and
26:08 Urinary bladder Hollow, muscular organ that serves as a temporary reservoir for urine
27:48 Urethra Extends from the neck of the bladder and carries urine out of the body Longer in men than in women External urethral sphincter – Voluntary control Urination
Please take the opportunity to connect and share this video with your friends and family if you find it useful.